Fujitsu announced the development of a resource toolkit offering developers guidance for evaluating the ethical impact and risks of AI systems based on international AI ethics guidelines.
Fujitsu will offer these resources free of charge starting from February 21, 2022 to promote the safe and secure deployment of AI systems in society.
The toolkit consists of a variety of case studies and reference materials, including a newly developed method for clarifying ethical requirements in AI ethics guidelines written in natural language, as well as for applying ethical requirements to actual AI systems. The resources in Japanese can be downloaded here, with availability in English to follow in the near future.
With this guidance, Fujitsu aims to prevent misunderstandings and potential risks caused by differences in the interpretation of descriptions in guidelines, offering AI system developers and operators new tools for thoroughly identifying and preventing possible ethical issues early in the development process in keeping with international best practices.
Dr. Christoph Lutge of the Technical University of Munich, a leading authority in the research of responsible AI and business ethics, comments,
"In Europe, there is a growing debate about AI regulations, and one of the key issues is how to close the gap between principles and practices, or "what" and "how." I believe that the results of this research are very significant in that they enable us to practice based on principles. I would also like to express my deep appreciation for the decision to open up the research results and stimulate discussion worldwide."
Going forward, Fujitsu will actively work to partner with government agencies, private companies, and leading researchers to further refine and promote its newly developed methodology and aims to release an expanded version of the resource toolkit in fiscal year 2022.
Background
In April 2021, the European Commission issued a draft for a regulatory framework calling for a comprehensive ethical response for AI system developers, users, and stakeholders in response to increasing concerns surrounding algorithmic bias and discriminatory decision-making in AI and machine learning applications.
To commit fully to the responsible use of technology and earn society's trust in AI systems and the companies and organizations involved in this space, Fujitsu has formulated its own AI Commitment in 2019, as well as a new AI Ethics and Governance Office to develop and enforce robust policies for AI ethics, promote organizational AI ethical governance to ensure their effectiveness. Now, Fujitsu will move from principle to practice by steadily implementing best practices in the real-world to ensure the realization of ethical, safe, and transparent AI and machine learning technologies.
At present, it is common practice in AI system development to identify possible ethical risks in AI systems based on AI ethics guidelines issued by government authorities and companies. These guidelines are written in natural language, however, contributing to possible differences in interpretation and misunderstandings amongst designers and developers that can lead to inappropriate or insufficient measures. Under this method it is also difficult to judge whether the contents of the guidelines were thoroughly and appropriately reviewed.
Many challenges remain, however, and possible misinterpretation of guidelines in the design phase of new technologies can potentially lead to insufficient or inappropriate measures to counter risk.
New evaluation method and resources to help clarify guidelines and ethical risk
In preparing this new toolkit and guidance for developers, Fujitsu performed analyses of past AI related incidents collected in the AI Incident Database of the international consortium Partnership on AI (1). This process led to the conclusion that ethical issues related to AI systems can be contextualized with the exchange of information ("interactions") between discreet elements within an AI system and between an AI system and its users and other stakeholders.
Based on these findings, Fujitsu successfully developed an evaluation method to systematically identify relevant ethical issues related to AI systems, allowing for the creation of AI ethics models (2) that are able to clarify the interpretation of AI ethics guidelines.
Fujitsu applied its new evaluation method to 15 representative cases out of the AI Incident
Database (164 global cases registered as of February 21, 2022, examples included cases from areas like the financial and human resources sector). Applying the new method, all ethical issues that occurred in real world use cases were successfully identified as risks in advance during verification trials, the results of which have been published.
Fujitsu will be offering the following resource toolkit consisting of a variety of resources and guidance for developers to refer to in their own work:
- Whitepaper: A general overview of methodology
- AI ethical impact assessment procedure manual: AI system diagram, preparation procedure of AI ethical model and explanation of problem correspondence method
- AI ethical model: An AI ethical model based on AI ethical guidelines published by the European Commission (created by Fujitsu)
- AI ethics analysis case studies: Results of analysis of major AI ethics issues from the AI Incident Database of Partnership on AI (As of February 21, there were six cases, which were added sequentially.)
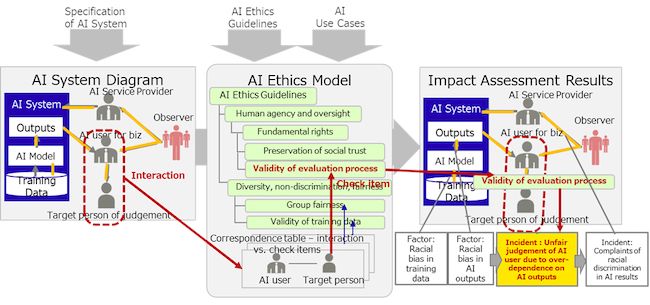
Use Case: risk in use of AI for the evaluation of individuals for bank loans, recruitment
Figure 1 shows an example of an evaluation process of an individual typical in use case scenarios like personnel recruitment or the approval of bank loans. The correspondence table in the AI ethics model identified the "validity of the evaluation process" (whether the evaluation is conducted responsibly with reference to the output results from the AI system) as a check item for the interaction (relationship) between the user of the AI system and the target person to be evaluated, whereas "overdependency on AI results," "selective interpretation and evaluation of output results" and "ignorance of output results" are listed as possible risks.
Within this example, AI system developers can identify the risk of an "overdependence of users on outputs from an AI system that may contain bias and lead to unfair decisions" as a possible risk in an AI system and appropriately adjust the system to prevent this risk.
(1) Partnership on AI:
A non-profit organization established in 2016 that address the ethical challenges of AI, for a future where AI and humans work together.
(2) AI ethics models:
AI ethics models include a correspondence table of "check items" and "interactions", a tool for step-by-step evaluation of ethical requirements for AI systems. AI ethic models are manually created based on a specific guideline, but once generated, a model can be used generically to evaluate various AI systems. Using this method, developers and operators of AI systems can automatically retrieve all relevant check items from a previously created AI ethics model for a systematic and comprehensive evaluation of related possible risks based on the type of interactions within an AI system.
News Source: JCN Newswire









