Content marketing strategy is a structured plan that guides the creation and distribution of content to support business objectives. According to the Content Marketing Institute, content marketing itself is "a strategic marketing approach focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience — and, ultimately, to drive profitable customer action." A content marketing strategy turns this approach into action by outlining the "why," "who," "what," "how," and "how to measure" behind every piece of content.
HubSpot describes it as a program centered on creating, publishing, and distributing content for a target audience, typically online, to attract customers. In 2026, this definition holds but adapts to new realities. AI tools generate drafts faster than ever, search engines deliver answers directly in summaries, and audiences demand transparency. A strong strategy ensures content remains human-centered, trustworthy, and aligned with goals amid these shifts.
Businesses create and follow content marketing strategies because they deliver measurable results over time. Organizations with documented strategies report stronger performance in lead generation, customer retention, and revenue growth. In B2B settings, for instance, 97% of marketers maintain a content strategy, and those who refine it see improvements in program effectiveness. Without a strategy, content efforts scatter, wasting resources on pieces that fail to connect or convert. A clear plan keeps teams focused, coordinates efforts across departments, and links content directly to outcomes like increased sales or lower acquisition costs.
1. Clear Business Goals and Objectives with KPIs

At its foundation, a content marketing strategy starts with specific business goals. These goals answer the question: What does the organization want to achieve through content? Common objectives include generating leads, building brand awareness, educating customers, or driving sales. Each goal pairs with key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress.
In 2026, clear goals matter more because AI can produce vast amounts of content quickly. Without defined objectives, teams risk creating volume over value. Goals also help navigate zero-click searches, where content must provide answers that build authority even if users never visit the site. E-E-A-T principles—Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—tie directly to goals, ensuring content demonstrates real knowledge rather than generic output.
Practical steps to implement this component begin with a workshop involving marketing, sales, and leadership teams. List three to five primary business goals for the year. For each, define one to three SMART KPIs (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound). Examples include website traffic from organic search, lead form submissions from gated content, or email open rates for newsletters. Assign owners and review progress quarterly.
A real-world illustration comes from a software company targeting IT managers. Its goal was to shorten sales cycles by 20%. KPIs included the number of downloads for comparison guides and the percentage of leads who engaged with educational webinars. The team tracked these in a shared dashboard, adjusting topics when engagement dipped.
This component integrates with 2026 trends through AI assistance. Tools analyze past performance to suggest goal-aligned topics, but humans set the direction. Trust-building appears in goals focused on transparency, such as publishing pricing details to foster credibility. For zero-click visibility, objectives emphasize creating clear, structured content that search summaries can quote accurately.
2. Defined Target Audience and Buyer Personas

Knowing who receives the content is e0o9ssential. A target audience includes broad groups, while buyer personas add depth by describing specific individuals within those groups. Personas capture demographics, behaviors, challenges, goals, and preferred channels.
This element stands out in 2026 because personalization at scale has become standard. AI helps segment audiences, but personas ground efforts in real needs. With rising focus on community and trust, personas highlight pain points that content can address authentically, strengthening E-E-A-T by showing deep understanding of the audience.
To implement, start with data collection. Review customer interviews, survey responses, website analytics, and sales notes. Create three to five personas, each with a name, photo, job title, daily challenges, and content preferences. Update them annually as behaviors shift.
Consider a B2C example from a fitness apparel brand. One persona, "Busy Professional Sarah," is 35, works in finance, values quick workouts, and reads short blog posts during commutes. Content for her includes five-minute video routines and email tips on recovery. In B2B, a manufacturing firm developed a persona for "Plant Manager Mike," who seeks efficiency data and case studies. Targeted whitepapers reduced his research time and increased inquiries.
Trends integrate here through AI for dynamic segmentation and community-driven insights. Platforms gather feedback to refine personas, while E-E-A-T shines when content references real experiences from similar audiences. Zero-click strategies benefit from personas that inform snippet-friendly answers to common questions.
3. Content Audit and Inventory
A content audit reviews existing material to identify strengths, gaps, and opportunities. An inventory catalogs all assets, including format, performance, and ownership.
In 2026, audits prevent duplication in an AI-heavy environment where low-quality content floods feeds. They ensure resources focus on high-value pieces that support E-E-A-T and appear in AI summaries. Regular audits maintain relevance amid fast-changing trends.
Steps involve listing all content in a spreadsheet or tool. Score each on criteria like traffic, engagement, alignment with goals, and freshness. Archive or update underperformers. Identify gaps by mapping content to the customer journey.
An e-commerce retailer audited its blog and found 40% of posts from three years ago ranked poorly. The team refreshed top performers with new data and visuals, boosting organic traffic by 35%. A nonprofit conducted an inventory and discovered strong video assets but weak email content, leading to a newsletter overhaul.
AI assists by scanning for duplicates or suggesting updates, but human judgment evaluates context and trust signals. This process supports zero-click visibility by prioritizing evergreen content that answers questions directly.
4. Messaging and Brand Voice
Messaging defines the key ideas the brand communicates. Brand voice describes the tone and style—professional yet approachable, for example.
This component gains importance in 2026 as audiences seek authenticity in a sea of AI-generated material. Consistent voice builds recognition and trust, core to E-E-A-T. Clear messaging ensures content addresses buyer concerns head-on, fostering loyalty.
Implementation starts with creating a style guide. Outline three to five core messages, such as "We simplify complex processes" or "Transparency drives better decisions." Define voice traits: friendly, expert, concise. Train all creators on the guide.
A financial services firm used messaging around "empowering everyday investors" in plain language. Its blog posts avoided jargon, leading to higher share rates. A tech hardware company maintained a straightforward, problem-solving voice in case studies, which resonated with decision-makers.
Trends connect through community approaches where voice invites dialogue, and AI tools check consistency while humans infuse personality for GEO (generative engine optimization), messaging crafts answers that AI systems cite reliably.
5. Content Types, Formats, and Creation Guidelines
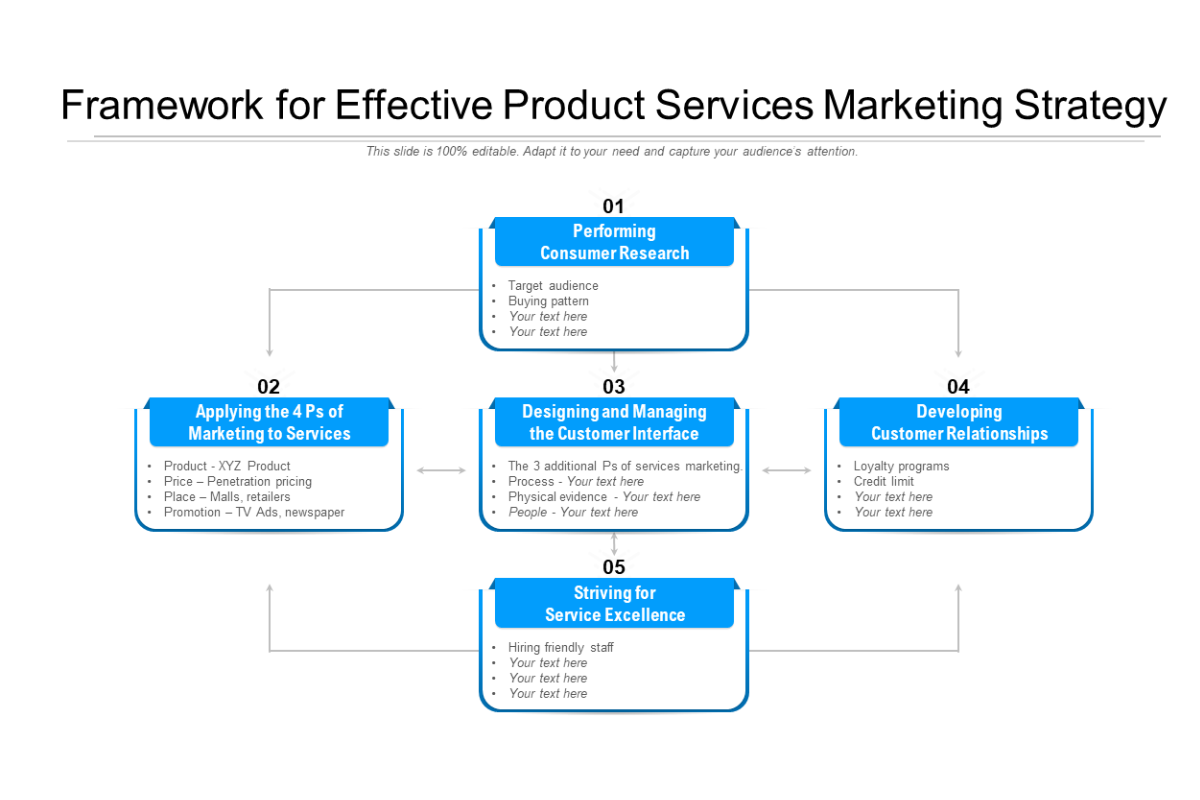
Content types include articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, and ebooks. Formats specify length or style, while guidelines cover quality standards, SEO practices, and processes.
In 2026, variety matters because preferences differ across platforms and devices. Guidelines maintain excellence when AI drafts content, ensuring it meets E-E-A-T and provides genuine value for zero-click contexts.
Practical steps: Brainstorm types based on audience and goals. Develop a creation playbook with templates, SEO checklists, and approval flows. Set standards for sources, visuals, and calls to action.
A B2B SaaS company mixed long-form guides with short LinkedIn videos and interactive tools. Guidelines required data-backed claims and author bios to highlight expertise. Results included stronger thought leadership. A consumer brand used user-generated photos in formats like carousels, guided by rules for authenticity.
AI integration speeds ideation and drafting, but guidelines emphasize human review for trust. Personalized formats, such as community Q&A threads, align with current directions.
6. Distribution Channels and Promotion Plan
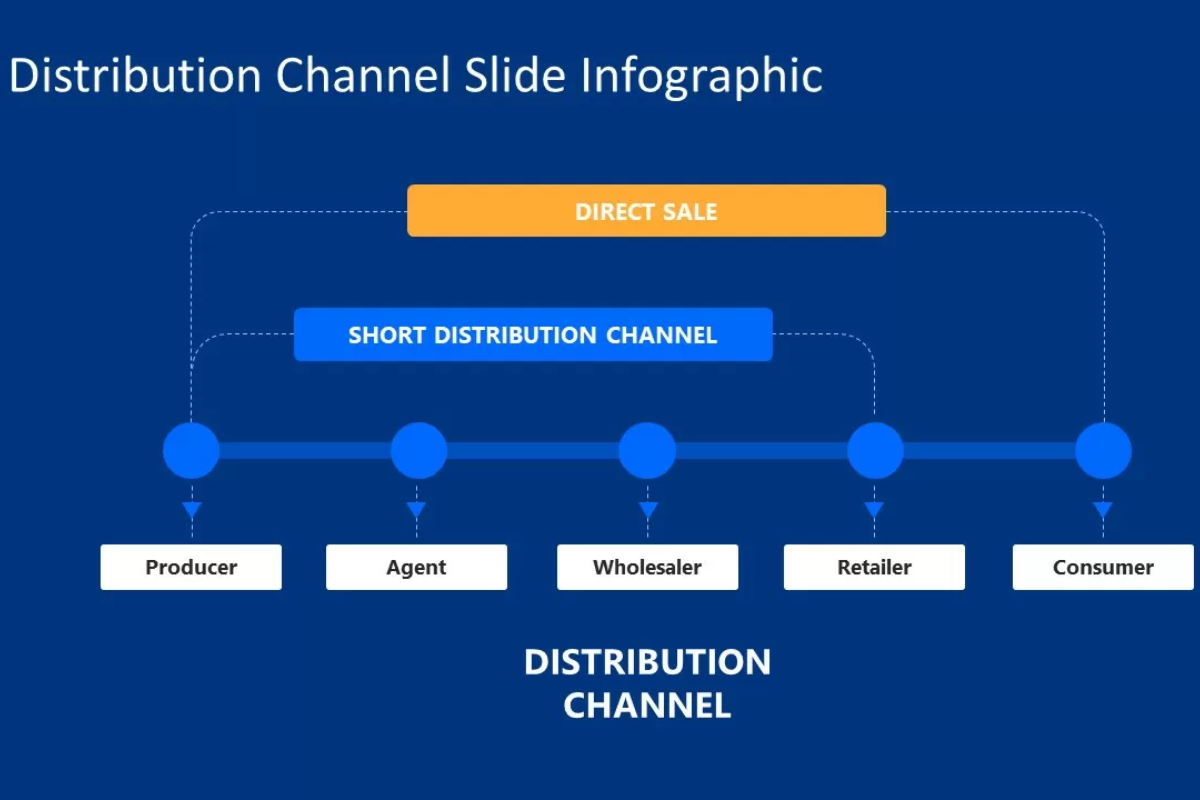
Distribution channels are the platforms where content reaches audiences: websites, social media, email, search, and partnerships. A promotion plan outlines paid amplification and organic sharing.
This matters in 2026 with fragmented attention and zero-click searches. Strategic distribution maximizes visibility in AI overviews and owned channels where trust builds directly.
Steps include mapping channels to personas and journey stages. Create a promotion calendar with organic tactics (shares, newsletters) and paid boosts. Test and refine based on reach.
A professional services firm distributed reports via LinkedIn and email, with targeted ads to industry groups. This drove webinar sign-ups. A retail brand repurposed blog content into Instagram Reels and Pinterest pins, increasing site visits.
Trends like community-driven sharing and GEO encourage formats optimized for snippets. AI tools predict best channels, but plans prioritize owned ecosystems for control and trust.
7. Editorial Calendar and Workflows
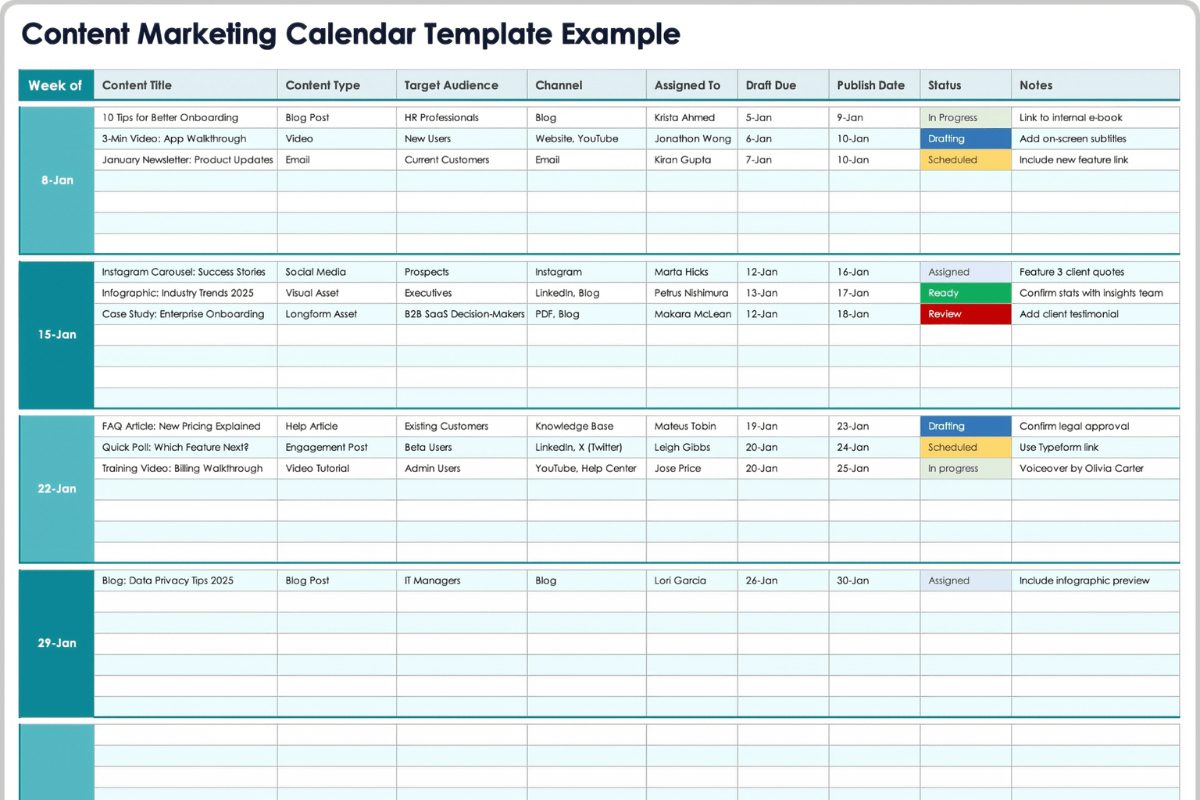
An editorial calendar schedules content creation and publication. Workflows define roles, deadlines, and tools for production.
In 2026, calendars prevent last-minute rushes amid AI-assisted workflows. They ensure steady output that builds momentum and E-E-A-T over time.
To build one, use a shared tool like a spreadsheet or project management app. Plan topics quarterly, assign tasks, and include buffers for reviews. Workflows map steps from ideation to publication.
A media company maintained a 12-month calendar with themes tied to seasons and industry events. Workflows assign writers, editors, and designers, reducing delays. A small business used a simple weekly calendar to alternate blog posts and videos.
AI populates calendars with topic suggestions, while workflows incorporate feedback loops for community input. This supports consistent presence for zero-click authority.
8. Measurement, Analytics, and Optimization Processes
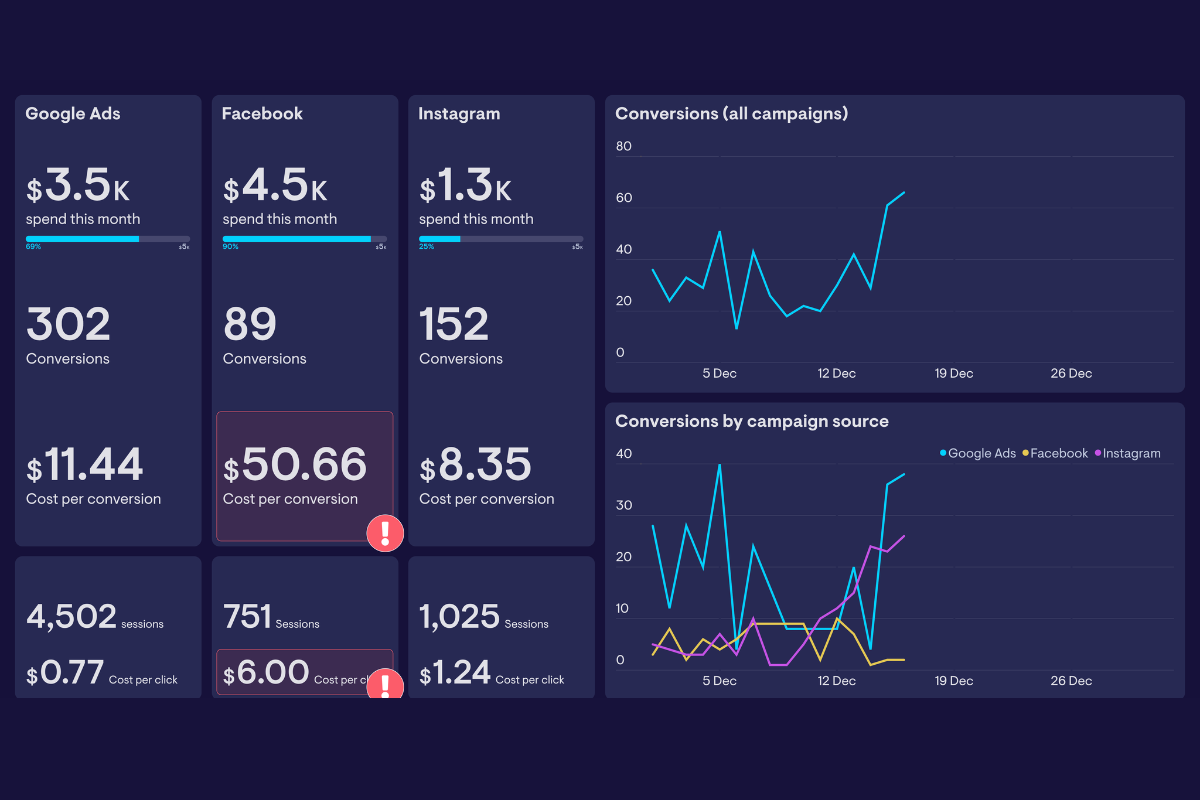
Measurement tracks performance against goals using tools like analytics platforms. Optimization involves reviewing data and adjusting tactics.
This component is critical in 2026 because AI generates data at high volume, but human insight turns numbers into decisions. Processes link content to revenue, proving value amid economic pressures.
Steps: Select tools for tracking (Google Analytics, CRM integrations). Define monthly reports on KPIs. Hold optimization meetings to act on insights, such as repurposing top content.
A B2C brand analyzed email metrics and found video thumbnails increased clicks by 40%. They optimized all campaigns accordingly. In B2B, a firm tied content attribution to closed deals, revealing webinars as a top converter.
AI dashboards automate reporting, but optimization focuses on trust metrics like time on page and share rates. E-E-A-T improves through iterative refinement based on audience signals.
Integrating Modern Trends into the Strategy
Effective strategies weave in 2026 trends without losing focus. AI integration boosts efficiency in research, drafting, and personalization, but guidelines require human oversight for quality and voice. Teams use AI for 80% of routine tasks while reserving creative and strategic work for people.
Trust ecosystems emerge as central. Content addresses buyer questions directly, including pricing and comparisons, to demonstrate expertise. E-E-A-T signals—author bios, sources, and real experiences—appear in every asset. Community-driven approaches encourage user contributions, building loyalty through dialogue.
Personalized experiences go beyond basic segmentation. Behavioral data triggers tailored sequences, such as follow-up emails based on content engagement. For AI search, known as generative engine optimization, strategies prioritize structured content, clear headings, and answer-focused formats that appear in summaries.
These elements connect back to core components. Goals include trust metrics, personas inform personalization, and measurement tracks AI-assisted outcomes.
Challenges in Building and Maintaining the Strategy
Common challenges include resource limitations, where teams juggle creation with distribution. Measurement complexity arises when linking content to long sales cycles. Differentiation grows harder as AI levels the playing field. Keeping content fresh amid trends demands ongoing effort.
Solutions focus on priorities. Start small with one documented strategy element, then expand. Use AI to handle repetitive tasks, freeing time for strategy. Cross-functional teams share measurement responsibilities. Regular audits and calendars maintain momentum. Training builds skills for E-E-A-T and community engagement. Many organizations allocate dedicated roles, such as content managers, to oversee the full process.
A content marketing strategy brings together defined goals, deep audience understanding, thorough audits, consistent messaging, varied content, smart distribution, organized calendars, and rigorous measurement. These components form a cohesive system that adapts to 2026 realities—AI efficiency, trust demands, personalized connections, and AI-driven search—while staying rooted in value.
Businesses that invest in this framework see content as a reliable engine for growth. It attracts audiences, builds lasting relationships, and delivers results over the years. By following these elements with discipline and openness to refinement, organizations create content that matters, connects, and contributes to long-term success.
Also read:















