The Arabian Desert is a vast, iconic landscape that stretches across the Arabian Peninsula. Covering over two million square kilometres, it's known for its endless sand dunes and rocky mountains. This desert is a place of history and culture, where ancient trade routes once thrived, and Bedouin tribes have lived for centuries. It's a region filled with unique plants and animals that have adapted to the harsh conditions.
In this article, we'll explore the geography, climate, and wildlife of the Arabian Desert. We'll also look at the people who live there, the natural resources found beneath its sands, and the challenges of conservation in such a harsh environment.
Geography
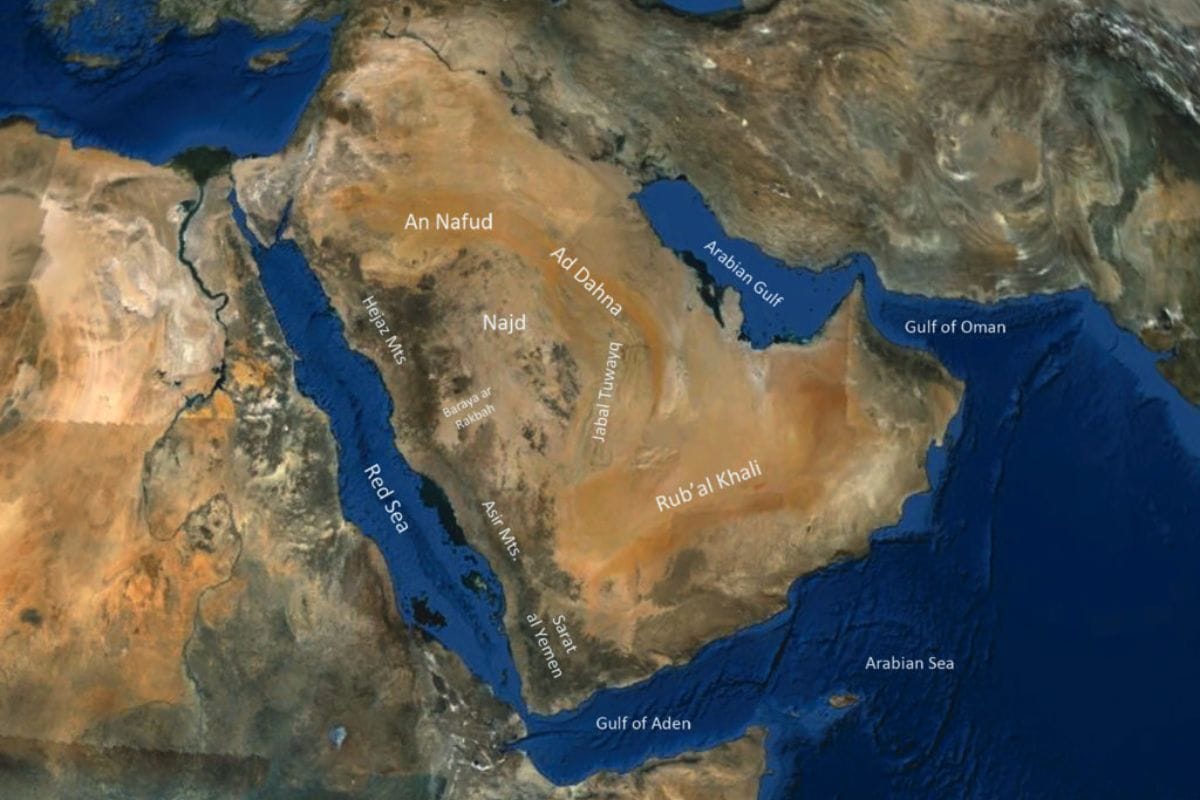
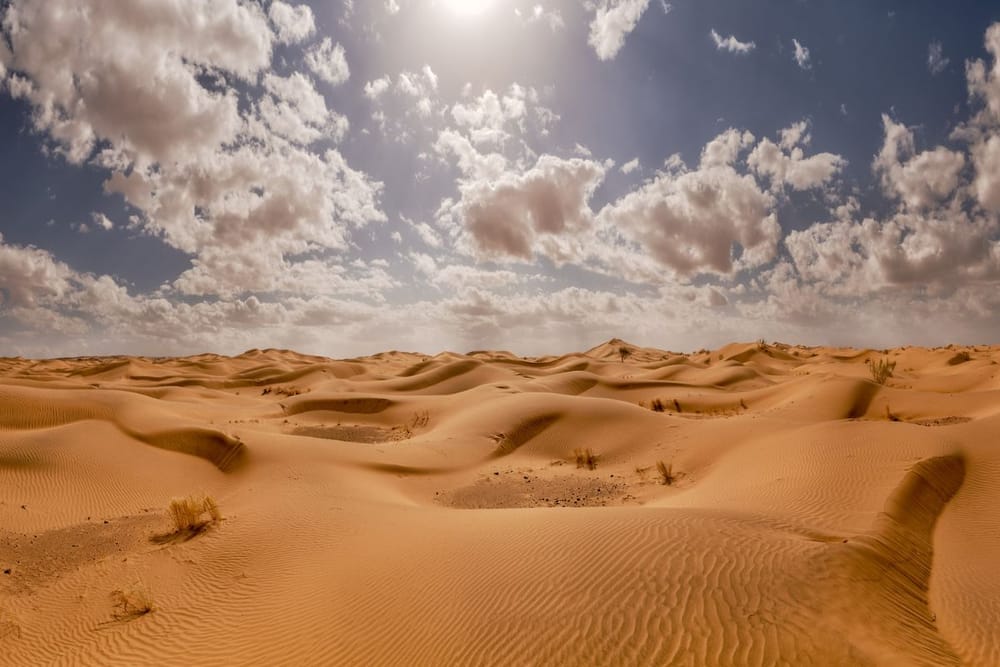
The Arabian Desert is a vast and iconic landscape that stretches across several countries in the Arabian Peninsula, including Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Kuwait, Iraq, and Jordan. Spanning approximately 2.3 million square kilometres, it is the largest desert in Asia and the fifth largest in the world.
Sand Seas and Gravel Plains
A defining feature is the Rub’ al Khali, the world's largest continuous sand desert, with dunes reaching up to 300 meters. These shifting sands contrast with the hamadas—gravel plains formed from ancient eroded mountains.
Mountain Ranges and Wadis
The desert also includes significant mountain ranges like the Al-Ḥajar in Oman and the Hijaz in Saudi Arabia. These areas offer a stark landscape of rocky terrain. Wadis, or dry riverbeds, occasionally come to life after rare rains, turning into green valleys for a short time.
Key Regions and Features
Key regions include An Nafud, with its red dunes, and the central Ad Dahna, a narrow sand corridor. The Rub’ al Khali, also known as the Empty Quarter, dominates the southern part of the desert. Oases like Tayma and Jubbah provide historical and cultural landmarks.
Unique Landscapes
The desert is not just about sand; it also features sabkhahs, or salt flats, especially near coastal areas. Lava fields, known as harra, mark the landscape with remnants of volcanic activity. The Jabal Tuwayq escarpment is a notable geological feature, stretching across central Arabia.
Climate

The Arabian Desert's climate is among the harshest, with extreme temperatures. Summers can reach over 50°C (122°F), while winters are milder, averaging around 20°C (68°F). Rainfall is scarce, often less than 100 millimetres (3.9 inches) annually, and quickly evaporates, leaving the land arid.
Seasonal changes bring occasional dust storms and sandstorms, particularly in spring and autumn. Coastal regions and highlands may experience higher humidity and occasional dew or fog, while the interior remains dry.
The desert's climate significantly shapes its landscape, with heat and wind eroding rocks and forming sand dunes. Rare flash floods can temporarily transform the terrain, supporting brief periods of vegetation.
Flora and Fauna
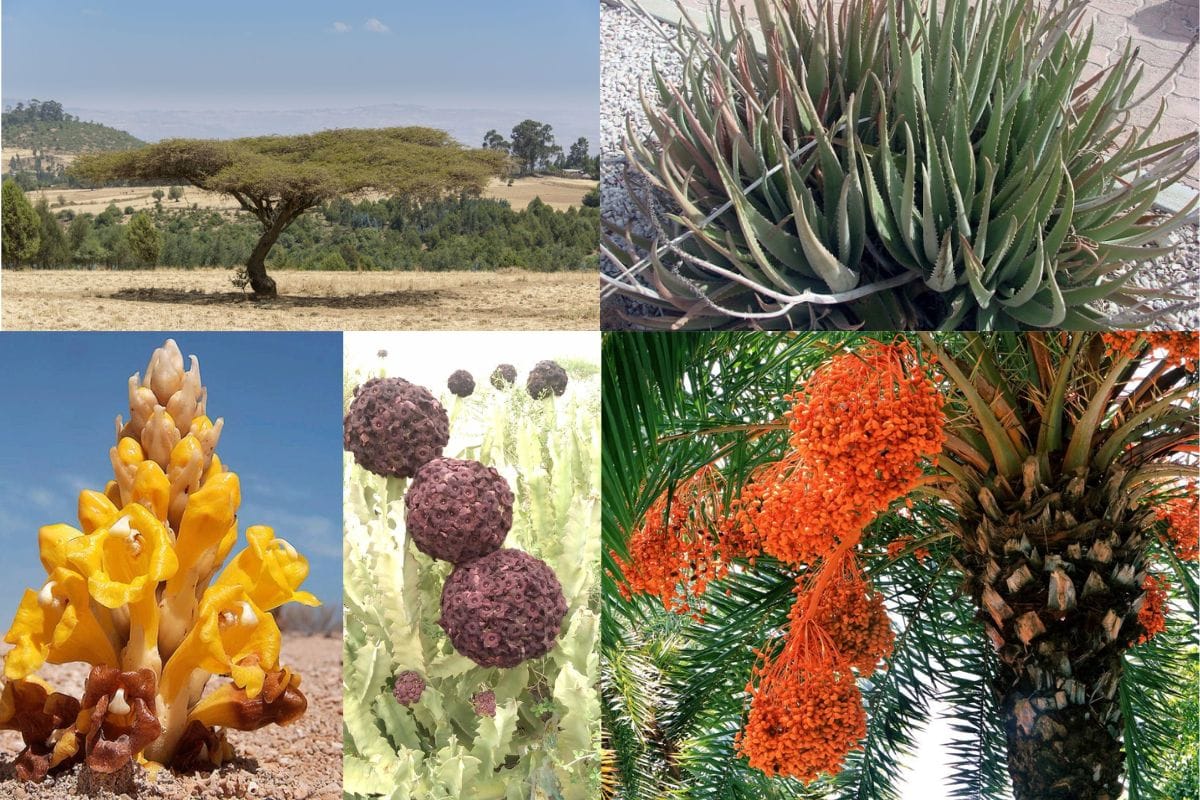



The Arabian Desert, despite its harsh conditions, supports a surprising variety of life. The flora includes hardy xerophytes and halophytes, plants adapted to limited water and high salinity. After rare rains, the desert blooms with a burst of greenery, including grasses, shrubs, and flowering plants like the desert rose and various types of succulents.
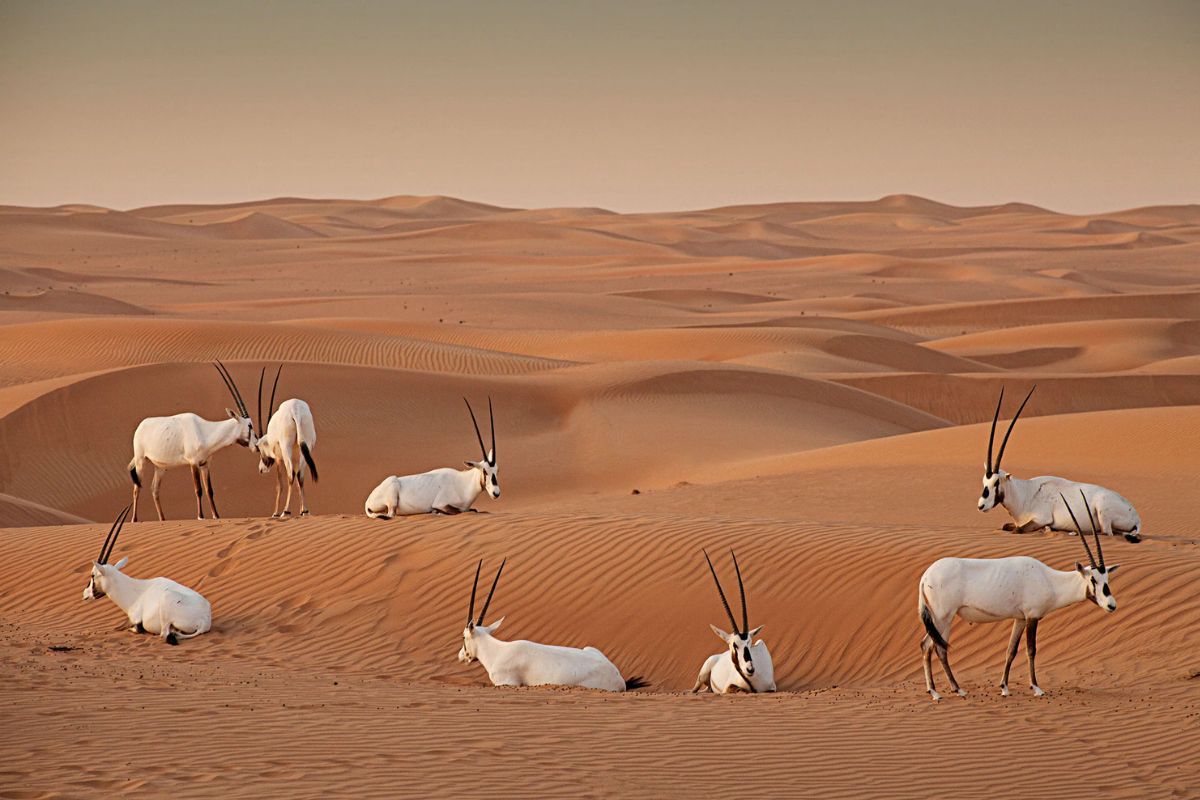
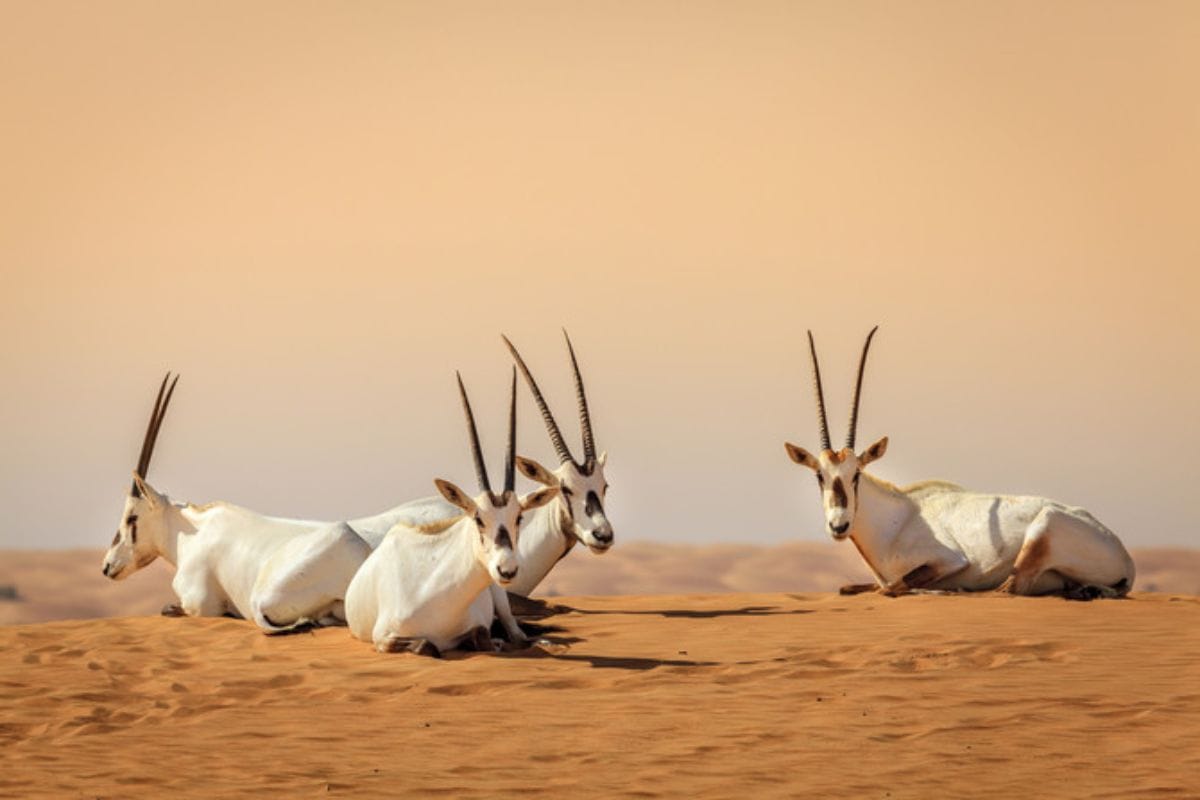
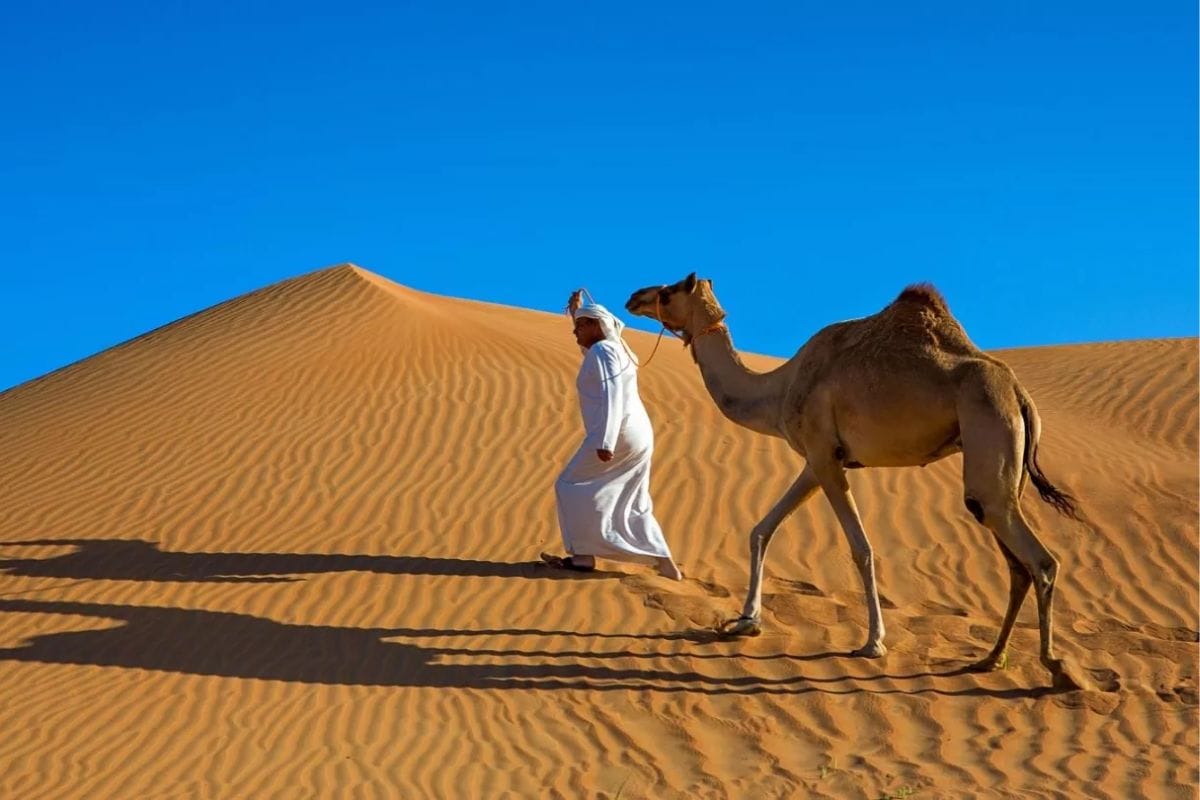
The fauna of the Arabian Desert is equally diverse. Many animals are nocturnal to avoid the extreme daytime heat. Notable species include the Arabian oryx, sand gazelle, and the iconic camel, known for its resilience and ability to go long periods without water. Smaller mammals like the jerboa, reptiles such as the sand viper, and numerous insects are also well-adapted to the arid environment. Birds, including falcons and sandgrouse, add to the desert's biodiversity, thriving in this challenging ecosystem.
People, Language, and Cultures
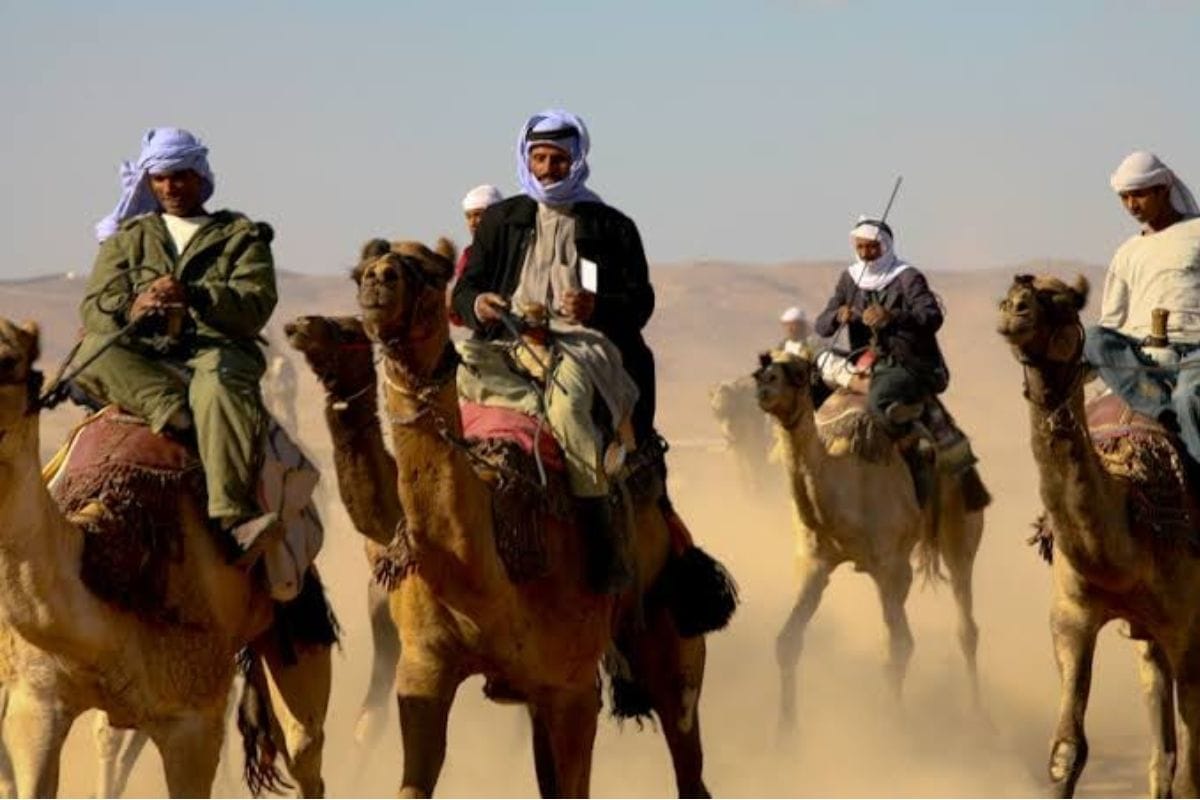
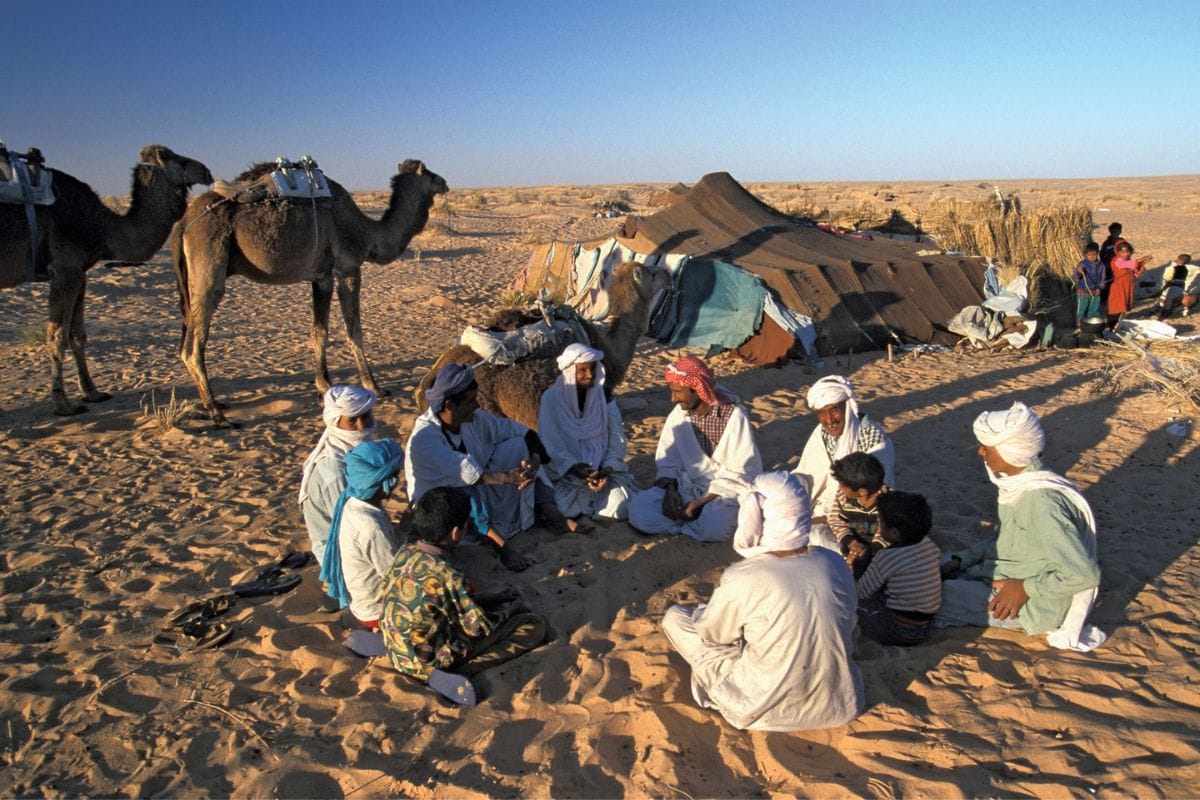


The Arabian Desert has been home to humans for thousands of years. The Bedouin tribes, known for their nomadic lifestyle, have historically dominated this region. These communities are renowned for their deep knowledge of the desert and their ability to survive its harsh conditions. Bedouin culture is rich in traditions, including poetry, music, and a strong code of hospitality.
Arabic is the primary language spoken across the region, with various dialects reflecting the diverse groups that inhabit the desert. Cultural practices are closely tied to the environment, with traditional crafts, cuisine, and clothing all designed to suit the desert lifestyle. The influence of Islam is profound, shaping social norms and cultural practices throughout the Arabian Peninsula.
Settlements


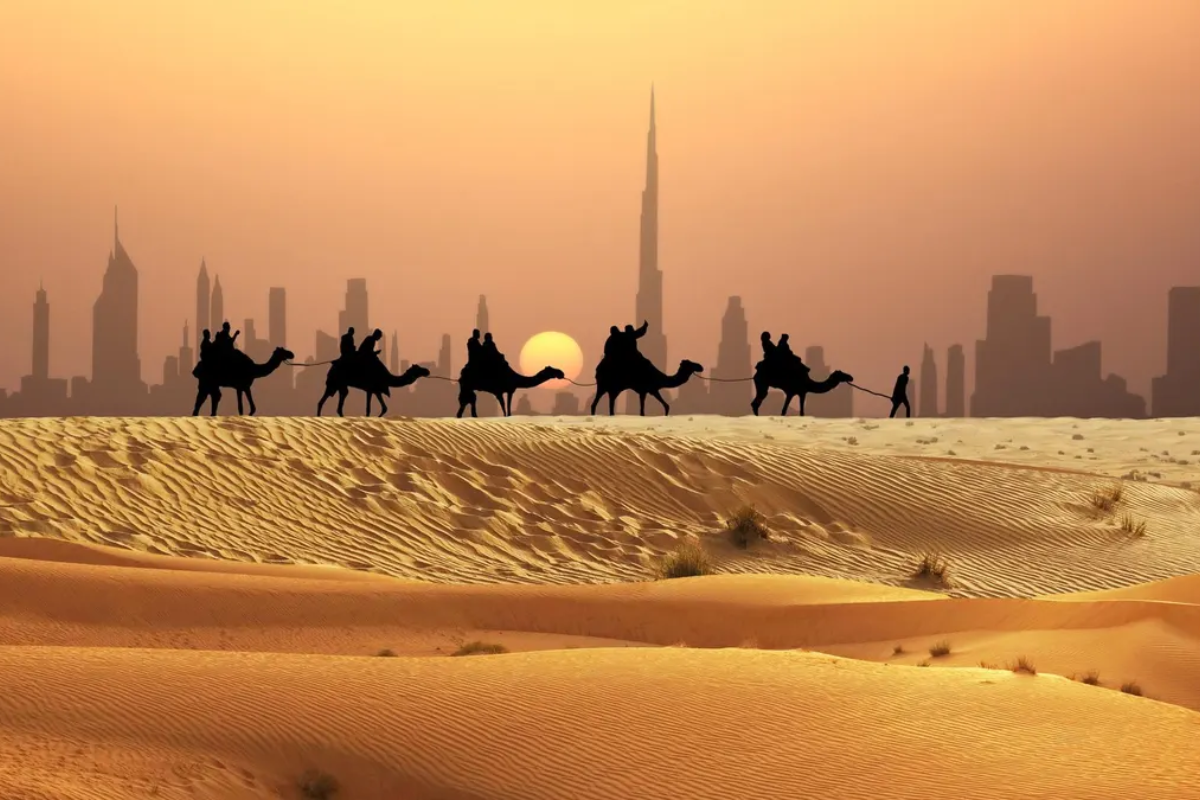
While much of the Arabian Desert remains sparsely populated, there are significant urban centers and historical settlements. Major cities like Riyadh, Dubai, and Muscat are located on the desert's periphery, blending modern development with traditional desert lifestyles. These cities have grown rapidly, fueled by economic opportunities, particularly in the oil and gas sectors.
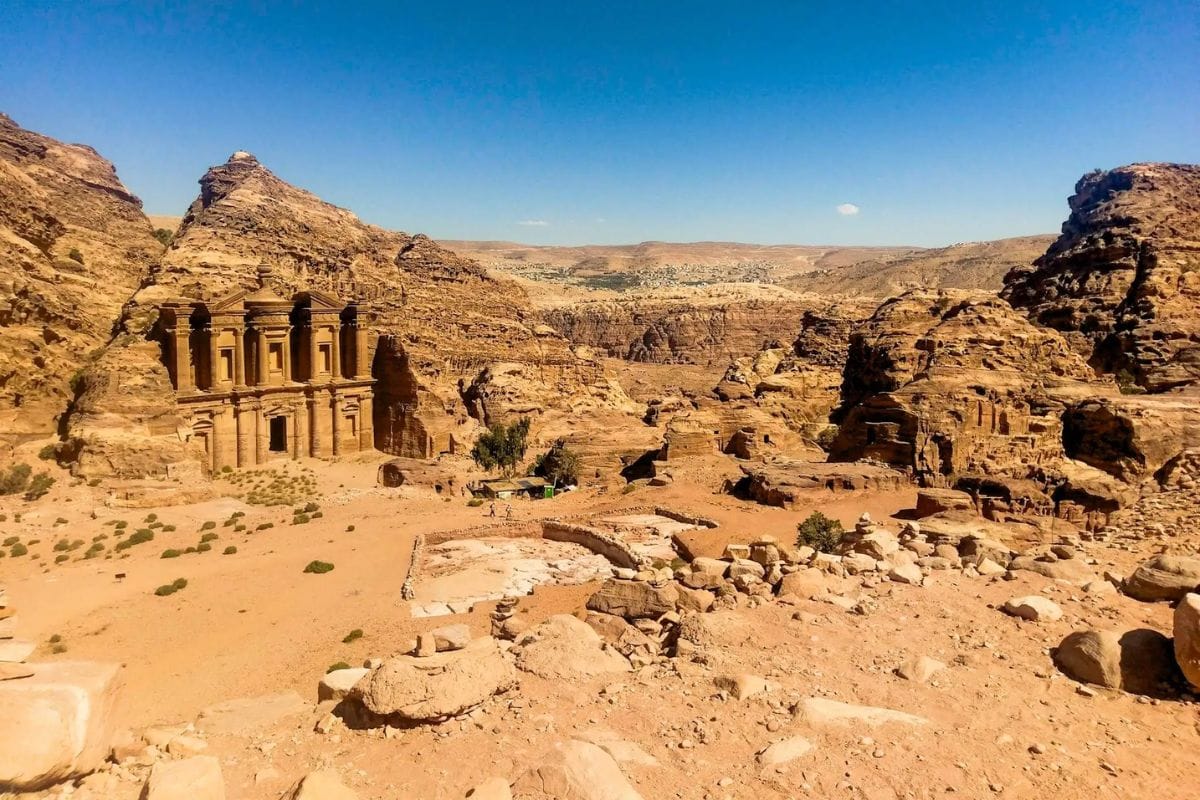
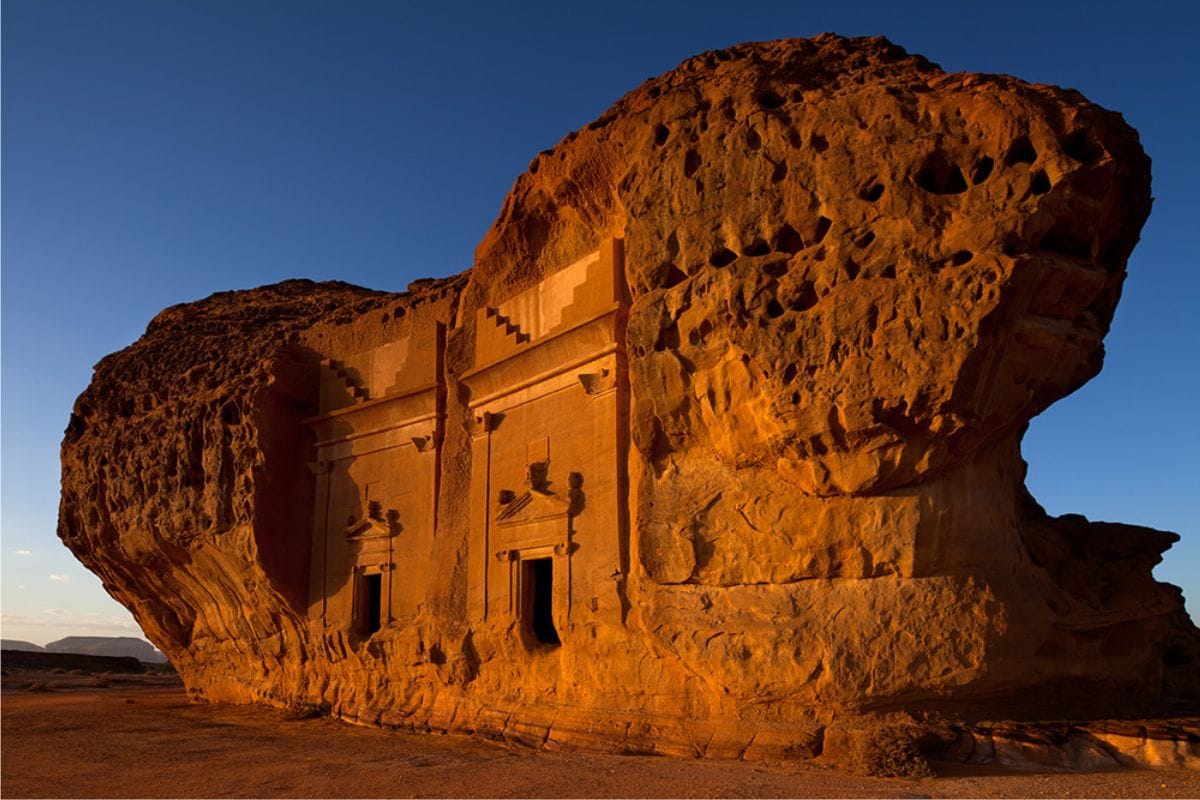
Oases such as Al Ain and ancient cities like Petra and Madain Saleh serve as historical landmarks, offering insights into the region's rich past. These settlements have traditionally served as critical hubs for trade, agriculture, and cultural exchange, providing life-sustaining resources in an otherwise inhospitable environment.
Natural Resources
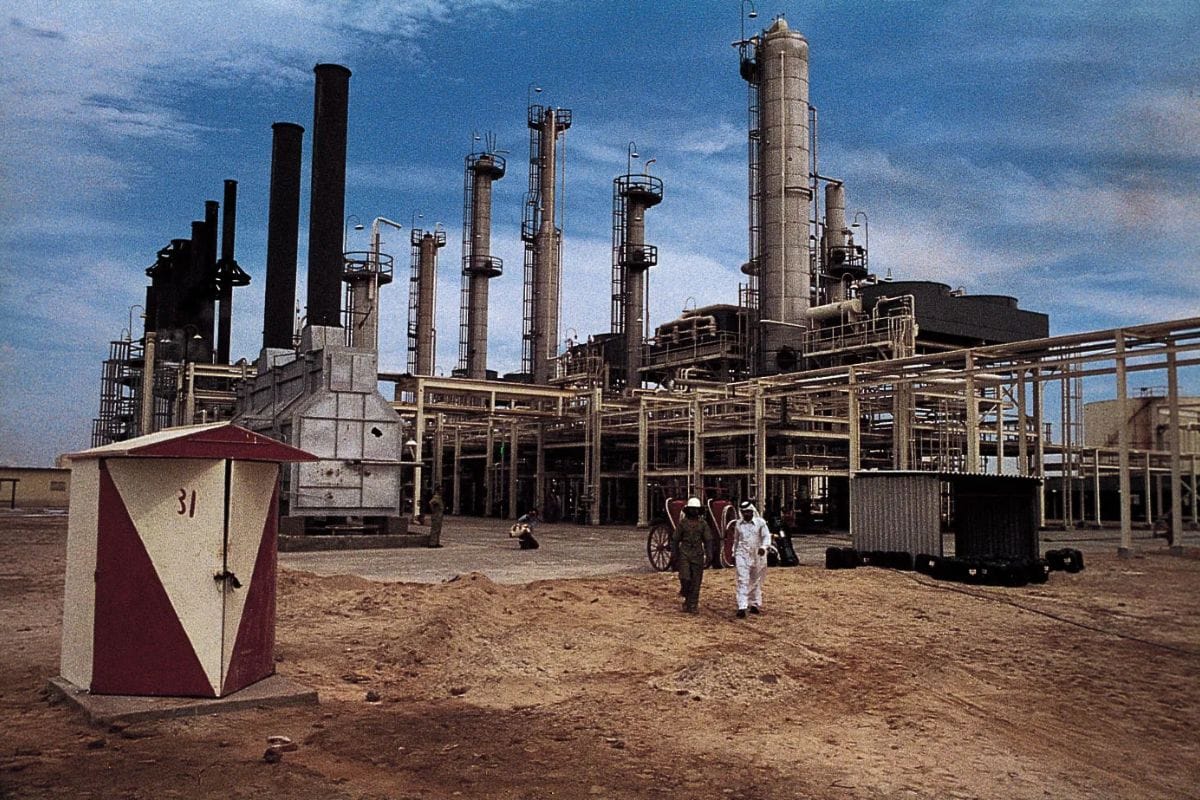

The Arabian Desert is rich in natural resources, most notably oil and natural gas. The discovery of vast oil reserves in the early 20th century transformed the region's economy, making it one of the wealthiest areas globally. The Al-Ghawar oil field, one of the largest in the world, lies beneath the desert sands.
Besides hydrocarbons, the desert also contains mineral resources such as phosphates, sulfur, and limestone. Water, a precious commodity in the region, is sourced from underground aquifers and increasingly from desalination plants along the coast. These resources have not only driven economic growth but also urbanization and infrastructure development in the region.
Conservation and Threats
The Arabian Desert faces several environmental challenges, including desertification, water scarcity, and habitat loss. Rapid urbanization and industrial activities, particularly in oil extraction, have significantly impacted the natural landscape. Efforts to combat these issues include conservation initiatives aimed at protecting endangered species like the Arabian oryx and regulating hunting and land use.
Conservation areas and wildlife reserves have been established to preserve the unique biodiversity of the desert. However, balancing development with environmental sustainability remains a critical challenge. Climate change poses an additional threat, potentially exacerbating water shortages and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events.
The Arabian Desert is a land of extremes and contrasts, rich in history, culture, and natural resources. From its vast sand dunes to its unique wildlife, the desert is a testament to the resilience of life in harsh conditions.
As the region continues to develop, it faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with the preservation of its natural and cultural heritage.
Also Read:















